WHO Collaborating Centers
Over 800 institutions in over 90 countries supporting WHO programmes...
The WHO Collaborating Centres (WHOCCs) are a highly valued mechanism of cooperation in which relevant institutions are designated by WHO to support the implementation and achievement of the Organization's planned strategic objectives at the regional and global levels:
- enhancing the scientific validity of its global health work;
- as well as developing and strengthening institutional capacity in countries and regions.
| DEFINITION: A WHO Collaborating Centre is an institution designated by the Director-General to form part of an international collaborative network carrying out activities in support of the Organization's programmes at all levels. |
WHO gains access to top centres worldwide and the institutional capacity to support its work and ensure the scientific validity of global health work.
Conversely, designation as a WHO collaborating centre provides institutions with enhanced visibility and recognition by national authorities, calling public attention to the health issues on which they work. It opens up improved opportunities for them to exchange information and develop technical cooperation with other institutions, in particular at international level, and to mobilize additional and sometimes important resources from funding partners.
History and present
The WHOCCs have been in place since the founding of the Organization. The first WHO CC was the Department of Biological Standardization, Statens Seruminstitute, Copenhagen, originally designated at the beginning of 1948; currently the Organization has over 800 WHOCCs located in almost 100 Member States.
Examples of recent designations are:
- Department of Medical Informatics Regenstrief Institute, Indianapolis, USA, designated in early 2009 as a WHO Collaborating Center for the Design, Application, and Research of Medical Information Systems. Their work with WHO is focused on the design, development, and implementation of enterprise medical record system architectures; use of standardized terminologies to facilitate health data interoperability, and the design and implementation of medical decision support systems.
- The Mycology Division, Department of Medical Microbiology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India, designated early 2009 as a WHO Collaborating Centre on Reference and Research on Fungi of Medical Importance. Their mission is to undertake collaborative research in epidemiology of fungal diseases, provide referral services for identification and characterization of emerging fungal infections, and maintain a collection of medically important fungi and supply these to investigators on request. They will also assist WHO in standardizing new diagnostic technologies and disseminate these to national laboratories, and providing technical support to member countries in establishing and managing fungal diagnostic services.
Eligibility and criteria for designation
An entire institution or, in most cases, a department, division or laboratory within an institution may be designated as a centre. Typical examples of WHO Collaborating Centres are departments of universities, laboratories or divisions of national research institutes, departments of hospitals, departments of ministries, national academies, etc.
To be eligible for designation, the proposed institution should have successfully worked with WHO in carrying out jointly planned activities.
The designation of new centres is subject to a strict review during which the following aspects are particularly assessed:
- the scientific and technical standing;
- the place the institution occupies in the country's health, scientific or educational structures;
- the institution's prospective stability in terms of personnel, activity and funding;
- the working relationship which the institution has developed with other institutions in the country, regional and global levels;
- the institution's ability, capacity and readiness to contribute to WHO programme activities;
- the technical and geographical relevance of the institution and its activities to WHO's programme priorities.
The designation is given on the basis of an agreed plan of work with WHO, which consist of a detailed list of concrete activities and products that the WHOCC will implement to contribute to the achievement of a WHO's task.
Examples of activities are:
- carrying out research for WHO;
- assisting in the development of a WHO guideline;
- gathering and analysing data for a WHO report;
- dissemination of information, providing a training course by request of WHO;
- standardization of terminology;
- provision of technical advice to WHO.
Designation and redesignation
The designation, which is originally given for a period of four years, is renewable for the same or shorter periods, if warranted by programme requirements and the results of evaluation. The redesignation process usually takes about 6 months. The redesignation should be approved before the date of expiry of the designation.
Designation is independent of financial support being given to the institution by WHO.
All centres are designated by the initiative of a WHO Department after successful completion of several years of collaboration with WHO in carrying out jointly planned activities.
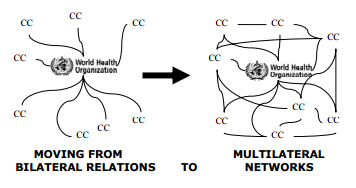
Networks of WHO Collaborating Centres
WHO Collaborating Centres are encouraged to develop working relations with other centres and national institutions recognized by WHO, in particular by setting up or joining collaborative networks with WHO’s support.
Through these global networks, the Organization is able to exercise leadership in shaping the international health agenda.
Examples of existing networks of Collaborating Centres are the Global Network of WHOCCs for nursing and midwifery development, the Network of WHOCCs on occupational health, and the Global Network of WHOCCs working on communicable diseases.
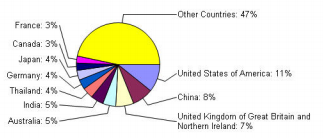
Countries and technical areas
As of 2009, the Member States with most centres are:
As of 2009, the technical areas with the most centres are: occupational health, health promotion, health systems research and development, mental health and neurosciences, nursing, health technologies, health information, statistics and measurement, reproductive heath, etc.
Find the Centres
The WHO Collaborating Centres Database is the official source of information about the WHO Collaborating Centres worldwide. It can be accessed here.
