Tuberculosis Surge in the Americas Demands Urgent and Innovative Action
The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) warns that the situation has been exacerbated by widening socioeconomic inequalities during the pandemic. Jarbas Barbosa, the organization's director, stresses the critical need to adopt new technologies to reverse this alarming trend.
Tuberculosis shows an uneven pattern of incidence, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations. Among the hardest-hit groups are incarcerated individuals – who account for up to 57% of cases in some countries – alongside indigenous peoples, homeless populations, and those with comorbidities or immunosuppressive conditions. Sylvain Aldighieri, PAHO's Director of Communicable Disease Control, highlights that approximately one-third of cases in Latin America are directly linked to prison systems, requiring targeted interventions in these settings.
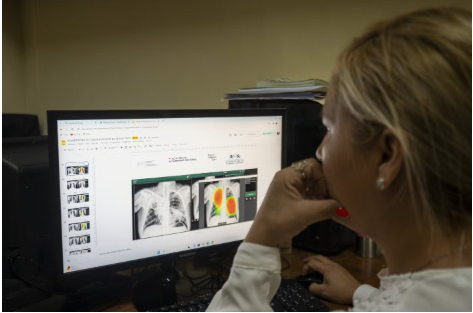
Facing this challenge, PAHO recommends implementing innovative strategies such as AI-assisted chest X-rays for screening – technology that has already proven effective by tripling detection rates in Peruvian prisons. Other measures include expanding rapid molecular testing in primary healthcare facilities and adopting shorter oral treatment regimens supported by telemedicine.
The global fight against tuberculosis gained momentum through commitments made by world leaders during the United Nations General Assembly meeting. PAHO and WHO emphasize the urgent need to translate these pledges into concrete action, focusing on strengthening national strategies, securing adequate funding, and overcoming gaps in access to prevention and treatment services.
As part of PAHO's Disease Elimination Initiative, tuberculosis ranks among the top 30 priority conditions for intervention, with efforts specifically targeting the most vulnerable populations. The current situation demands coordinated efforts and sustainable investments to curb the disease's advance and reverse the growth observed over the past decade.



