A third of pregnant women with COVID-19 unable to access life-saving critical care on time
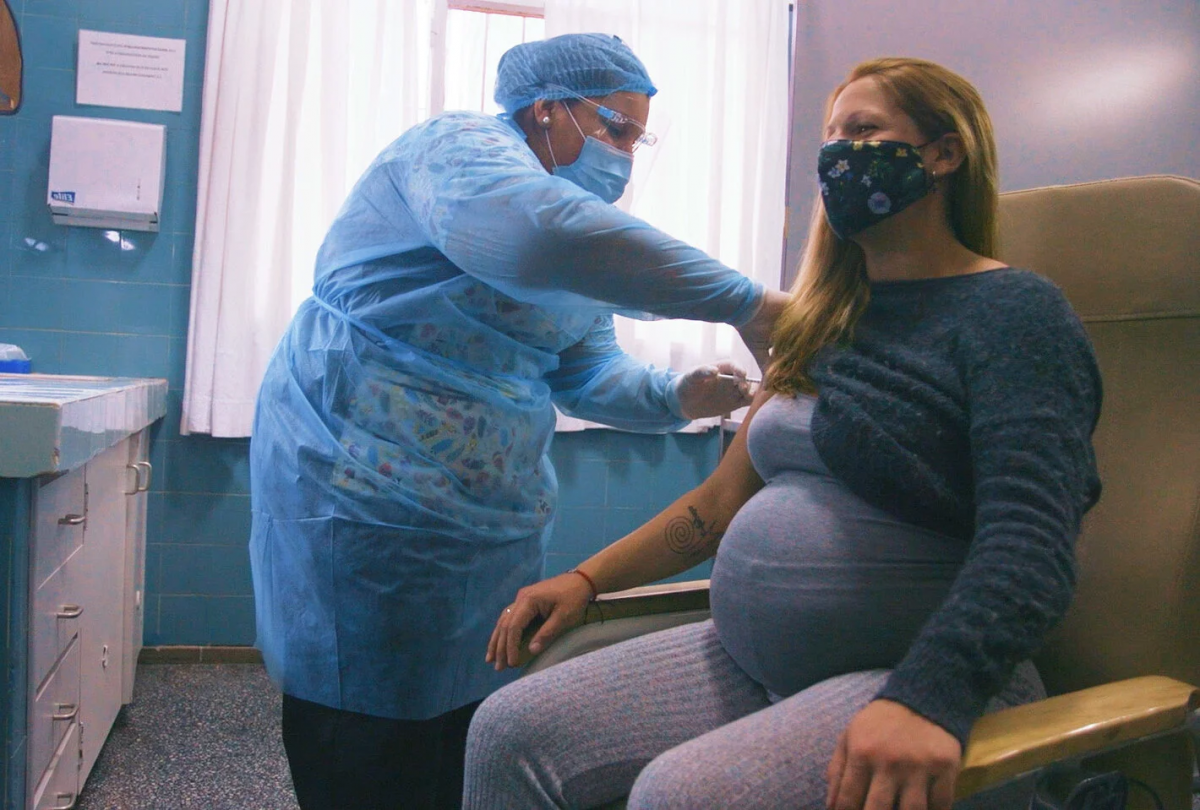
A lack of access to timely care and disruptions to prenatal services are to blame for an increase in maternal mortality in the Americas during the pandemic, with one in three pregnant women unable to access timely critical care, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) Director Carissa F. Etienne said.
With COVID-19 cases among pregnant women reaching more than 365,000 in the region over the past two years, and deaths surpassing 3000, Dr. Etienne said in a media briefing today that “this is a tragedy, especially now that we have safe and effective vaccines.”
A pre-published PAHO study on maternal mortality across 8 countries showed that from 447 pregnant women that died between 1 March 2020 and 29 November 2021, 90% were already experiencing life-threatening symptoms when admitted to hospital. Nearly 77% delivered their babies prematurely and 60% were born with low birth weight – an issue that can impact the health of a child for the rest of its life.
“We must prioritize women to ensure they are shielded from the worst of the pandemic,” Dr. Etienne said. Pregnant women, in particular, are “among the most vulnerable to COVID-19, due to changes in their immune system which can put them at risk for severe disease,” she added, urging countries to urgently ramp up access to vaccines, ensure the continuation of health services that women depend on, and improve access to family planning services.
These are “life-saving services that should remain open now more than ever,” added the Director.
Even though most countries in the region recommend COVID-19 vaccination for pregnant women, their uptake is still very low. “It is critical that health workers talk to expectant mothers about the importance of getting vaccinated to protect them, and their babies, from this virus,” Dr. Etienne said. The PAHO Director also called for greater emphasis on programs that address women of ethnic minorities, such as afro-descendants, indigenous women, and migrants who “are often at greater risk, due to the overlap of gender and social factors.
Dr. Etienne also highlighted the broader impact that the COVID-19 crisis has had on women and girls, including additional caregiving responsibilities and career disruptions.
She highlighted that – as the majority of the health workforce – women have been on the frontlines of the COVID-19 response, accounting for 72% of all COVID-19 cases among health professionals.
“In a region that is rife with inequality, women have, once again, been disproportionately affected,” she said.
Turning to the COVID-19 situation in the region, the Director reported that new cases dropped to 32% from the previous week, reaching 1.5 million. Countries also reported 24,650 deaths, a 10% decline.
These downward trends were seen throughout much of the region, with the exception of Central America where deaths rose by nearly 16% this week.



